链表
Jump to Section
两数相加 @leetcode 2
各个位置上的结点相加并需要考虑进位
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/AddTwoNumbers2.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
public class AddTwoNumbers2 {
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode last = head;
int pre = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int l1Val = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int l2Val = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
last.next = new ListNode((l1Val + l2Val + pre) % 10);
pre = (l1Val + l2Val + pre) / 10;
last = last.next;
if (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
// 注意此处的进位
if (pre != 0) {
last.next = new ListNode(pre);
last = last.next;
}
last.next = null;
return head.next;
}
}
}
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 @leetcode 19
使用双指针,cur 指向当前结点,pren 指向 cur 的第前 n 个结点,当 cur 走到 null 时,pren 即为需要删除的结点
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/RemoveNthNodeFromEndOfList19.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
public class RemoveNthNodeFromEndOfList19 {
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode p = head;
ListNode preOfPren = null;
ListNode pren = null;
while (p != null && n > 0) {
n--;
p = p.next;
}
if (n > 0) {
return null;
}
preOfPren = dummy;
pren = head;
while (p != null) {
preOfPren = pren;
pren = pren.next;
p = p.next;
}
preOfPren.next = pren.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素 II @leetcode 82
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedListII82.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
public class RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedListII82 {
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
if (next == null) {
tail.next = cur;
tail = tail.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else if (cur.val != next.val) {
tail.next = cur;
tail = tail.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
cur = findNextUnDuplicatedNodeWithHead(cur);
}
}
tail.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
/**
* find the node closest to the head with different value example: 1->2->2 return 2 example:
* 2->2->3 return 3 example: 1->1->1 return null example: null return null
*
* @param head of the list
* @return the node closest to the head with different value or null
*/
ListNode findNextUnDuplicatedNodeWithHead(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
if (head.val != head.next.val) {
return head.next;
}
return findNextUnDuplicatedNodeWithHead(head.next);
}
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素 @leetcode 83
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedList83.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
public class RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedList83 {
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == pre.val) {
cur = cur.next;
pre.next = cur;
} else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
}
移除链表元素 @leetcode 203
- 增加一个 dummy 结点使删除头结点和中间结点的逻辑一致
- p 总是指向当前需要做逻辑判断的结点, pre 则为 p 的前一个结点
- p 指向的结点 val 与给定一致时,删除 p 结点,即 pre.next = p.next
- pre 与 p 的维护:当结点删除,下一轮的 pre 不需要变动,p = p.next,否则一直保持 pre 和 p 的前进
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/RemoveLinkedListElements203.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
public class RemoveLinkedListElements203 {
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode p = head;
while (p != null) {
if (p.val == val) {
pre.next = p.next;
} else {
pre = p;
}
p = p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
}
环形链表 II @leetcode 142
哈希法
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/LinkedListCycleIIHash.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class LinkedListCycleIIHash {
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
public class Solution {
private Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode p = head;
while (p != null) {
if (set.contains(p)) {
return p;
}
set.add(p);
p = p.next;
}
return null;
}
}
}
快慢指针
该思路比较有趣, 具体如下: 若存在环时, 遍历永不结束。慢指针每次走 1 步, 快指针每次走 2 步, 成环时快指针总是能追上慢指针。那么如何知道入口点, 由已知关系得:
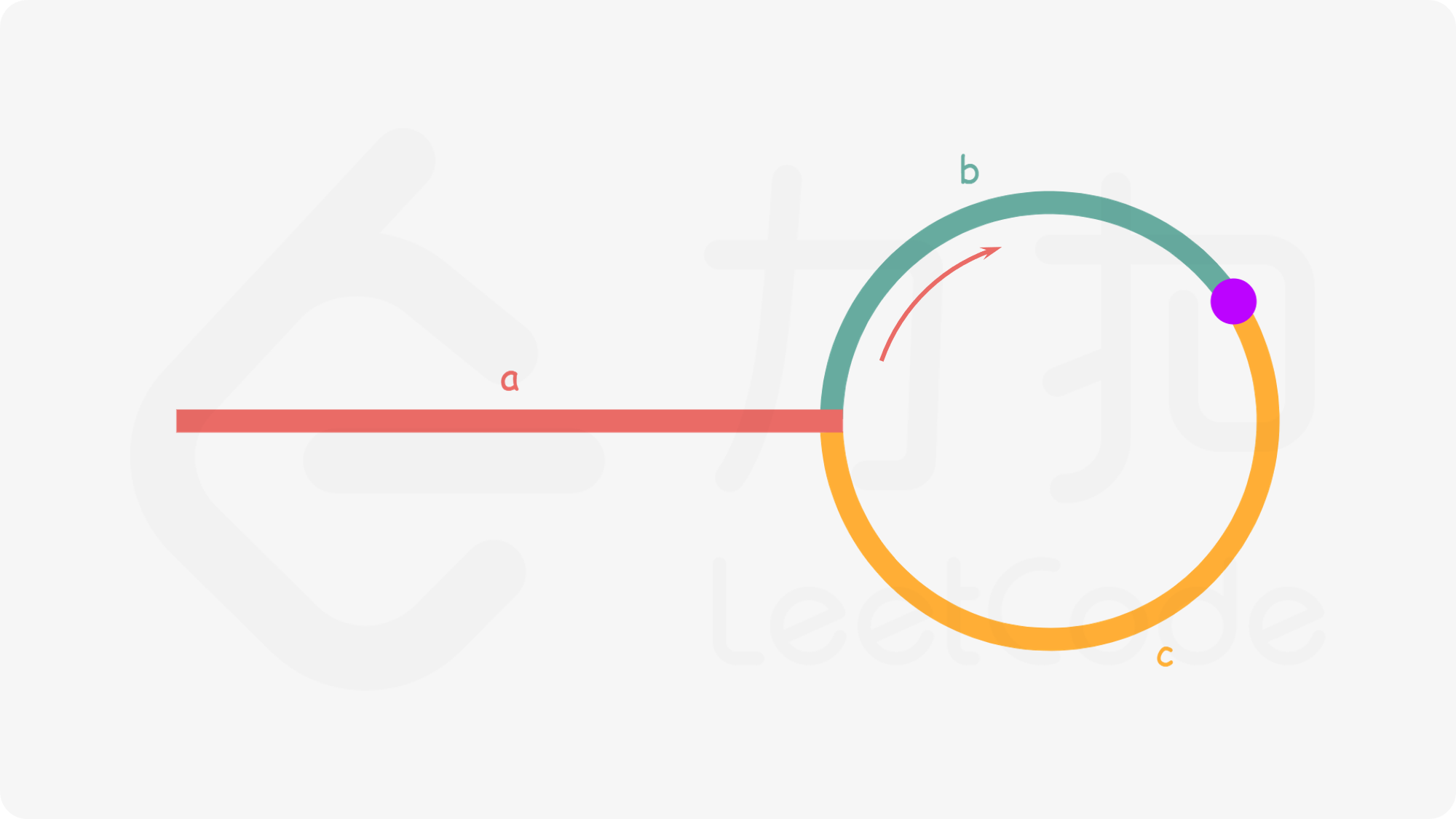
快指针路径长 = 2 倍慢指针的路径 = n 圈路径长 + a + b
2(a+b) = a+b+(b+c)*n
a+b = (b+c)n
a = (b+c)n-b
a = (b+c)(n-1)+c
从相遇点到入环点的距离加上 n-1 圈的环长,恰好等于从链表头部到入环点的距离
在表头新建指针与 slow 同步移动, 相交处即为入口点
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/LinkedListCycleIIDoublePoint.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
public class LinkedListCycleIIDoublePoint {
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow, fast, find;
try {
find = head;
slow = head.next;
fast = slow.next;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
return null;
}
while (fast != null) {
if (fast == slow) {
while (find != slow) {
find = find.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return find;
}
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
} else {
return null;
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
两数相加 II @leetcode 445
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/AddTwoNumbersII445.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
public class AddTwoNumbersII445 {
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class Solution {
private ArrayDeque<ListNode> pushToStack(ListNode l) {
ArrayDeque<ListNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
while (l != null) {
stack.push(l);
l = l.next;
}
return stack;
}
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ArrayDeque<ListNode> stack1 = pushToStack(l1);
ArrayDeque<ListNode> stack2 = pushToStack(l2);
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
head.next = null;
int carry = 0;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()) {
int s1 = stack1.pop().val;
int s2 = stack2.pop().val;
head.next = new ListNode((s1 + s2 + carry) % 10, head.next);
carry = (s1 + s2 + carry) / 10;
}
ArrayDeque<ListNode> stack = stack1.isEmpty() ? stack2 : stack1;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int val = stack.pop().val;
head.next = new ListNode((val + carry) % 10, head.next);
carry = (val + carry) / 10;
}
if (carry > 0) {
head.next = new ListNode(carry, head.next);
}
return head.next;
}
}
}
设计链表 @leetcode 707
- 维护 dummy 为链表的初始结点,维护 tail 指针指向链表末尾非 null 结点(初始化时 tail = dummy),维护 len 代表当前链表的长度(不计 dummy)
- 何时更新 tail 指针?
- addAtHead(val) 或 addAtIndex(-1, val) 且插入的结点为头结点,更新 tail 为当前插入的结点
- deleteAtIndex(index) index 为链表的尾结点,更新 tail 为删除结点的 previous 结点
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/DesignLinkedList707.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
public class DesignLinkedList707 {
class MyLinkedList {
private Node dummy;
// tail refs to last one of the list
private Node tail;
private int len;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyLinkedList() {
dummy = new Node(-1);
tail = dummy;
}
/**
* Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1.
*/
public int get(int index) {
Node p = dummy.next;
if (index < 0 || index >= len) {
return -1;
}
while (index > 0) {
p = p.next;
index--;
}
return p.val;
}
/**
* Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the
* new node will be the first node of the linked list.
*/
public void addAtHead(int val) {
Node pre = dummy;
Node p = dummy.next;
pre.next = new Node(val, p);
len++;
if (p == null) {
tail = pre.next;
}
}
/** Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. */
public void addAtTail(int val) {
Node node = new Node(val);
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
len++;
}
/**
* Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the
* length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is
* greater than the length, the node will not be inserted.
*/
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
Node pre = dummy;
Node p = dummy.next;
if (index < 0) {
this.addAtHead(val);
return;
}
if (index > len) {
return;
}
if (index == len) {
this.addAtTail(val);
return;
}
while (index > 0) {
index--;
pre = p;
p = p.next;
}
pre.next = new Node(val, p);
len++;
}
/** Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. */
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
Node p = dummy.next;
Node pre = dummy;
if (index < 0 || index >= len) {
return;
}
while (index > 0) {
index--;
pre = p;
p = p.next;
}
pre.next = p.next;
len--;
if (p.next == null) {
tail = pre;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
Node p = this.dummy.next;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
while (p != null) {
sb.append(p.val + "->");
p = p.next;
}
if (tail == null) {
sb.append("null] tail: null");
} else {
sb.append("null] tail:" + tail.val);
}
return sb.toString();
}
class Node {
private int val;
private Node next;
public Node(int val) {
this(val, null);
}
public Node(int val, Node next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
}
合并 K 个升序链表 @leetcode 23
合并 2 个升序链表的逻辑,在其基础上扩展合并 K 个
// ../../../../src/main/java/com/dll/linkedList/MergeKSortedLists23.java
package com.dll.linkedList;
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class MergeKSortedLists23 {
class Solution {
ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1, null);
ListNode last = head;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
last.next = new ListNode(Math.min(l1.val, l2.val), null);
last = last.next;
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
if (l1 == null) {
last.next = l2;
} else {
last.next = l1;
}
return removeHeadIfExist(head);
}
private ListNode removeHeadIfExist(ListNode head) {
return (head.val == -1) ? head.next : head;
}
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode previousMerged = null;
for (ListNode list : lists) {
previousMerged = mergeTwoLists(previousMerged, list);
}
return previousMerged;
}
}
}